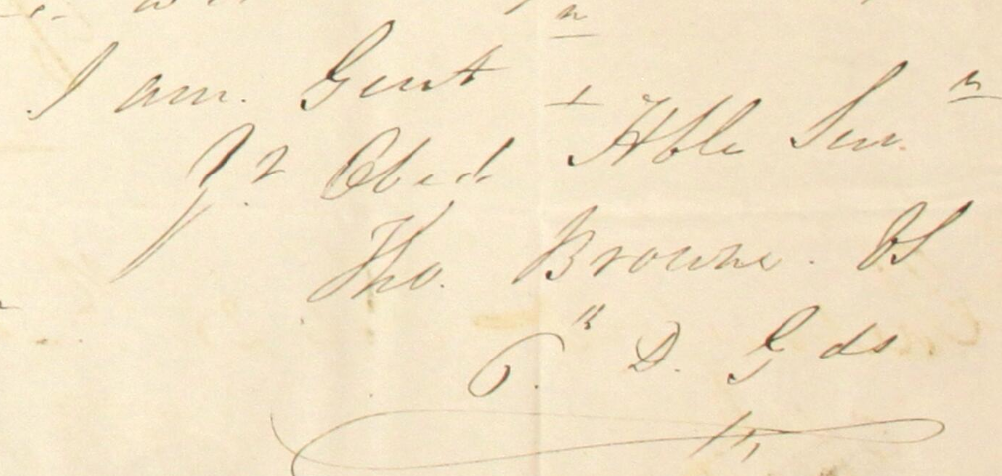Cataloguing the Correspondence of Henry Gray
As the RCVS Knowledge Archives and Digitisation assistant, my main duties are to scan the historical material, upload it to our Digital Collections website and take part in the promotion of the collection. In recent months, I have worked on a side project: cataloguing the personal correspondence and research papers of veterinary surgeon Henry Gray (1865-1939).
One of the most enjoyable parts of cataloguing Henry Gray’s material is not just the insights into past veterinary practice, but also the veterinary surgeons behind that practice. I spend one day a week delving into his professional and personal life; building up a picture of his character, and his ideals, through the correspondence he received from his peers.

Portrait of Henry Gray
Henry Gray qualified from the London Veterinary College in 1885 and set up a practice in Kensington on Earls Court Road (pictured below), though sadly this original facade no longer exists.

Henry Gray pictured in front of his surgery in Kensington
Henry Gray’s daughter bequeathed his materials to the RCVS in 1955 and now I get the satisfying task of reading, cataloguing and ordering his letters, postcards, research, and notes. It’s a fascinating insight to the work of a veterinary surgeon in the early 20th century and through these letters, I get detailed opinions from Gray’s peers regarding the state of the veterinary profession. I also find out about the diseases they were researching at the time. There is also correspondence from doctors studying human medicine, because there was often cross-over between human and animal disease, Henry Gray would consult the work of doctors and vice versa.
There aren’t many letters in Gray’s own hand and there is little biographical information about him, but I still build up a strong picture of his character from the letters he received. Gray was described as ‘pugnacious’ and, in letters written to him, his friends would often challenge him on his critical nature. What I admire most about this man was his very clear passion for his profession and his concern for the treatment of animals. He was not only relied upon for his expert opinion on animal treatments, but he was also an avid writer. Gray’s main correspondent was E. Wallis Hoare, the editor of ‘Veterinary News’, who relied upon Gray’s research and writing as content for the journal. Gray also wrote his own papers and was an extremely busy and dedicated man, eventually becoming the editor of the ‘Veterinary News’ himself. Gray was widely read, multilingual, and translated important veterinary works from French and German to English for his peers. Gray was known to be fond of saying:

Gray held this belief in high esteem and from what I have found, he had a real thirst for knowledge and shared it with his peers as often as he was able.
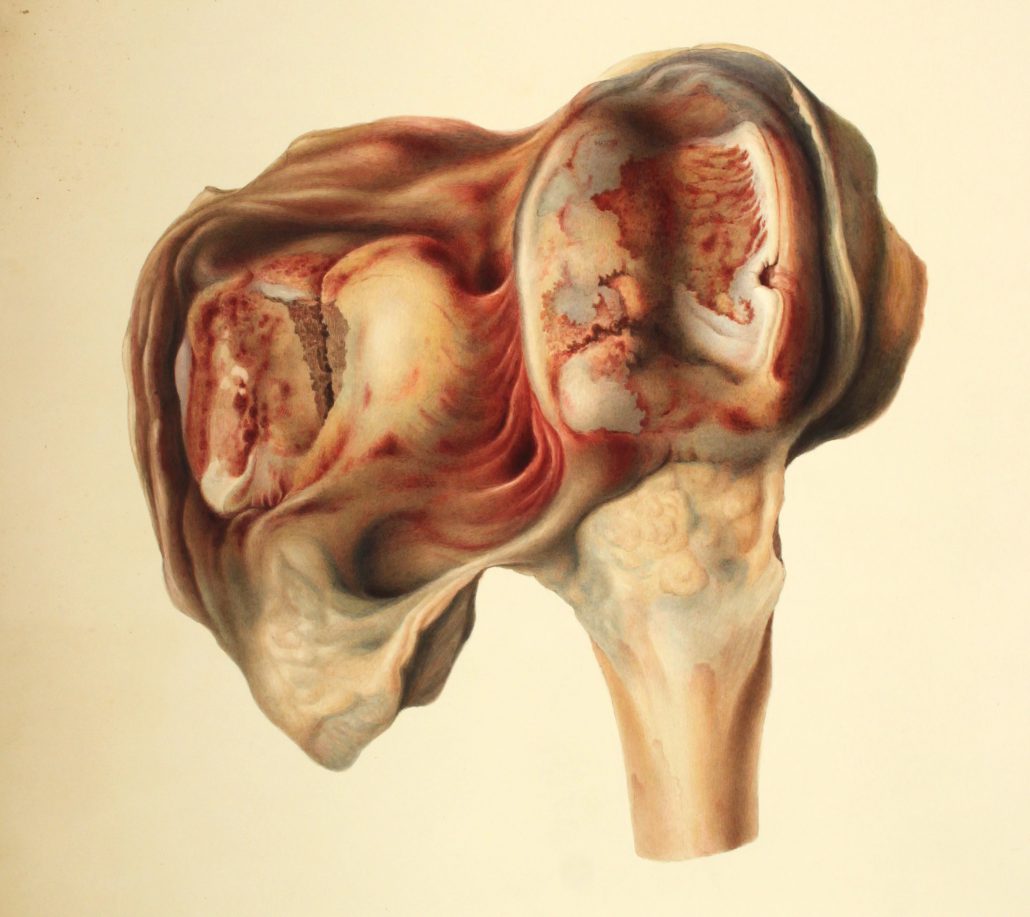
The breadth of topics he researched, and the topics that interested him, seems exhaustive to me – though he did specialise. Gray became an expert on birds and established one of the first practices that specialised in small animals. He donated some very beautiful books to the library here at RCVS, my favourite is pictured below.

The Speaking Parrots by Dr. Karl Russ (1884)
One of the most surprising things, at least to me, is that vets did not feel respected. Gray’s main correspondents were incredibly dissatisfied with the state of the profession. Gray and Hoare were forward-thinking men who were interested in the progress of veterinary science and education, though Hoare was so dismayed by the men already within the profession, he often discouraged people to enter it. Hoare believed that their work made a better hobby than a living. I have found some quotes in the letters that convey some of the feeling of the time.
“Had I been a Solicitor or Doctor an Engineer or a Tradesman etc – I should have been married ages ago but a horse doctor, a dog doctor … is no catch”
– A. Cholet
The above quote appears in the letter pictured below (which includes a match making request!):

Other notable comments include:
“I am proud of having been an apothecary and medical man, and nearly always ashamed of being a veterinary surgeon”
– H. Leeney
The RCVS was often a favourite topic in the letters and got its fair share of criticism; mainly concerning the education of veterinary surgeons. One remark in a letter questioned why exams for doctors were days long whilst the RVC exam was over in a few hours. Another comment concerned the females of the profession – specifically Aleen Cust. E. Hoare, who was incredibly progressive, was very outspoken about the attitudes of the council. He writes in one letter:
“ The Lady V.S in Roscommon; I hope to get her to write some articles and show the antiquated members of the council what a woman can do…”
– E. Hoare
I really admire the degree to which these men cared about their work and the reputation of the profession as a whole.
Another significant aspect of cataloguing this collection concerned the time period that most of the letters were written, which was during the First World War. I’ve read firsthand accounts of how the army treated the veterinary surgeons trying to care for their horses. The image below is a section of a letter written by H. Leeney; he rebukes Gray for his critical ways, but also goes in to detail about working for the army.

There are also passing comments within the letters on major events of the time, such as the sinking of the Lusitania, and these are juxtaposed with the cases they are tackling in their own practices (away from the fighting). My favourite part of working with Gray’s personal archive is that are many facets to the collection. The material is not all clinical and scientific. I also learn about the obstacles the vets faced due to the fact that certain technology was not available. The image below is a snippet of a letter from E. Hoare where he describes his troubles chloroforming a horse.

“I tried chloroforming standing on a big horse last Monday and shall not attempt it again”
– E . Hoare
Throughout this project I am finding out a great deal about the veterinary profession. Getting to know Gray (and his peers) has helped me understand the challenges and similar circumstances they faced, and how this compares to the present day. It definitely continues to strike me how the members of this profession never wish to stop learning, their intellectual natures and how innovative they continue to be, and often have to be. I am very much looking forward to putting this collection online! Please follow on Instagram where we add our favourite finds from the archives and historical collections.
Helena